Frequently Asked Questions
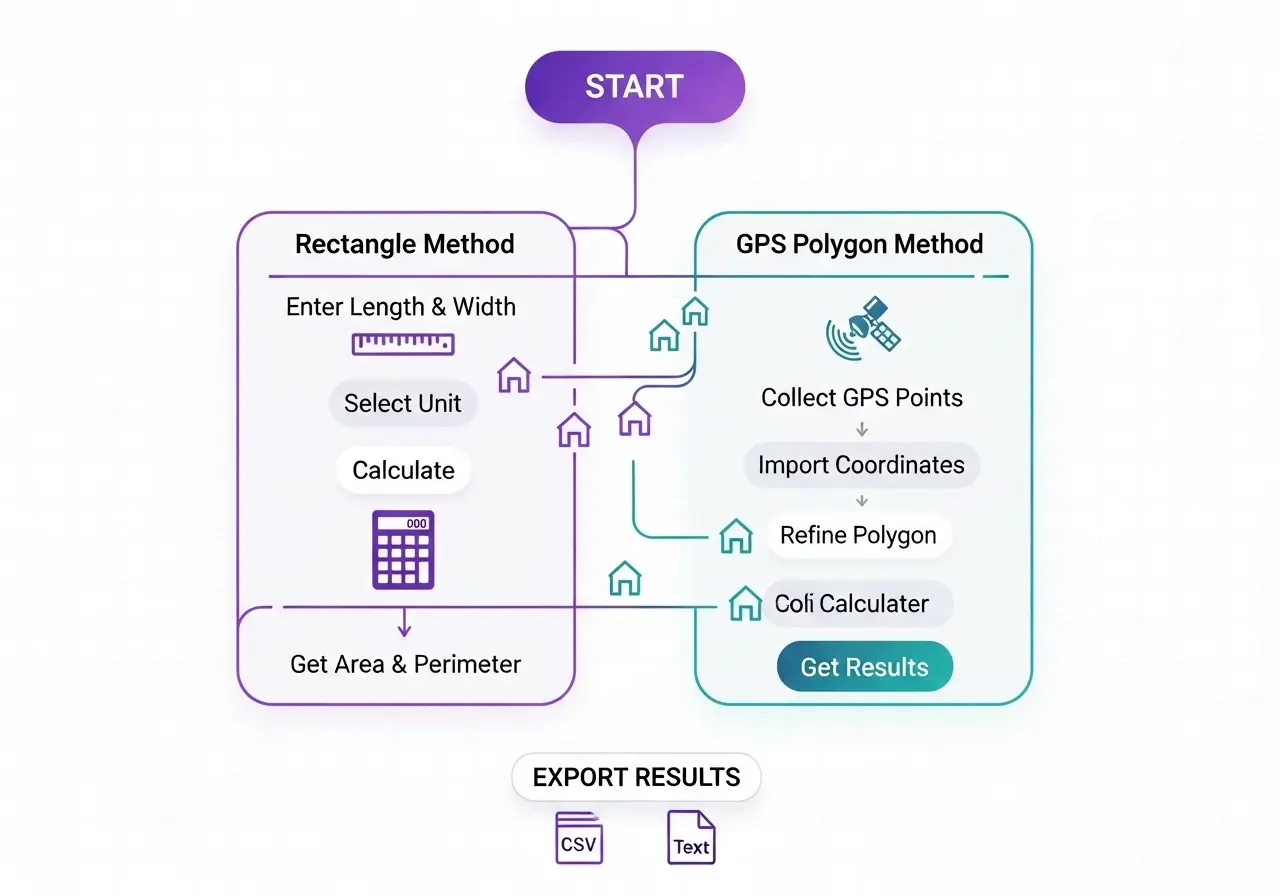
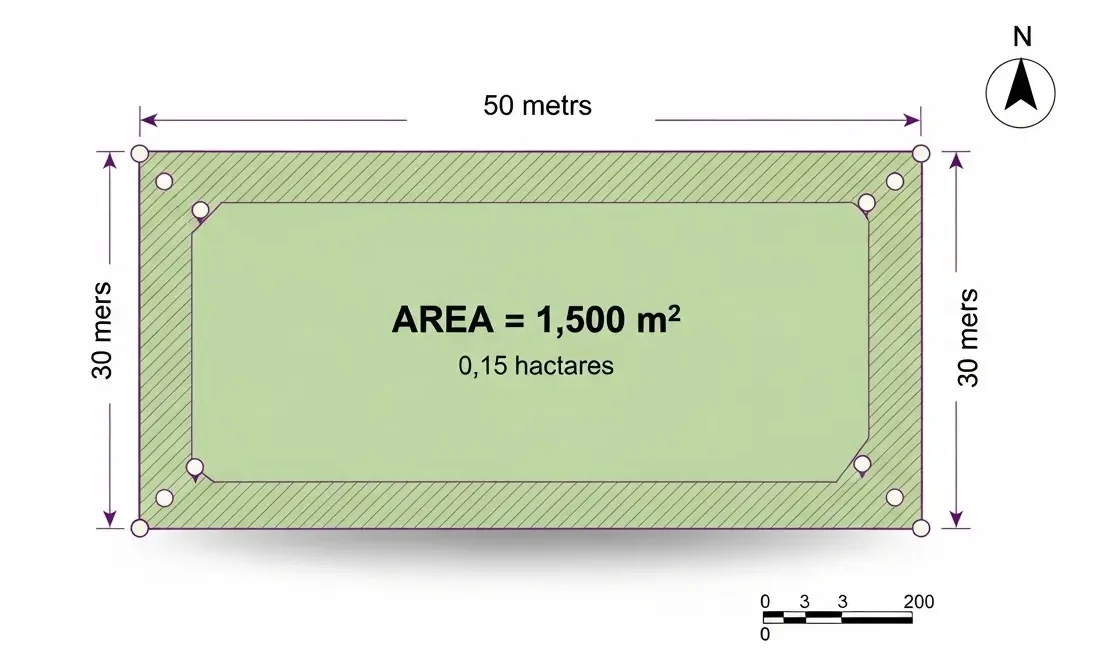
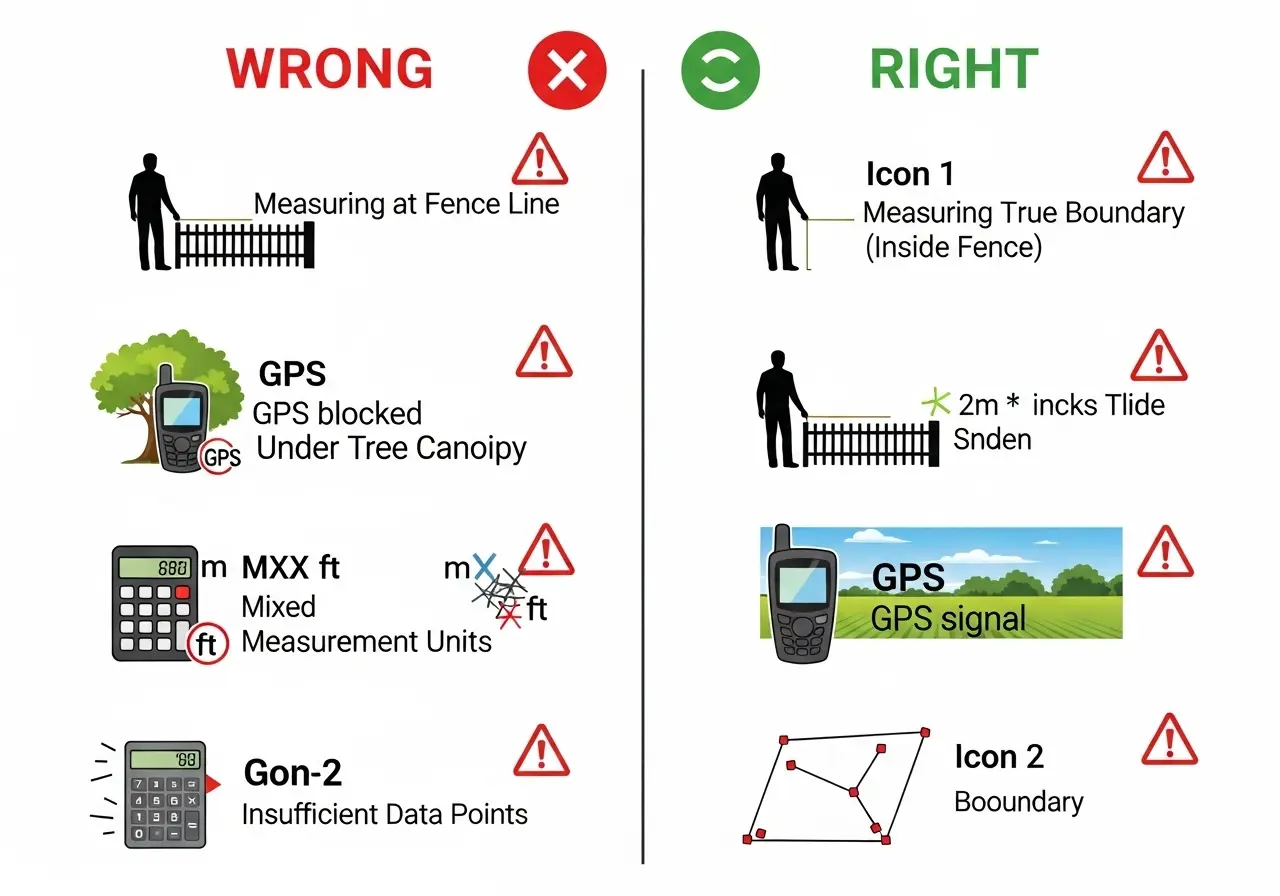
The most accurate method for irregular plots is using GPS coordinates with the polygon calculation method. Professional surveyors achieve ±2-5 cm accuracy using RTK GPS. For everyday use, smartphone GPS provides ±3-10 meter accuracy, sufficient for fields larger than 0.5 hectares. Rectangle calculation using measured dimensions works best for regular shapes and can be accurate to ±1% if dimensions are carefully measured.
Yes, Google Maps allows area measurement, but it's less convenient than dedicated calculators. Right-click on the map, select "Measure distance," then click around your property boundary. However, Google Maps doesn't provide coordinate export, offline functionality, or easy unit conversion that specialized land area calculators offer. For occasional use it works; for repeated measurements, dedicated calculators are superior.
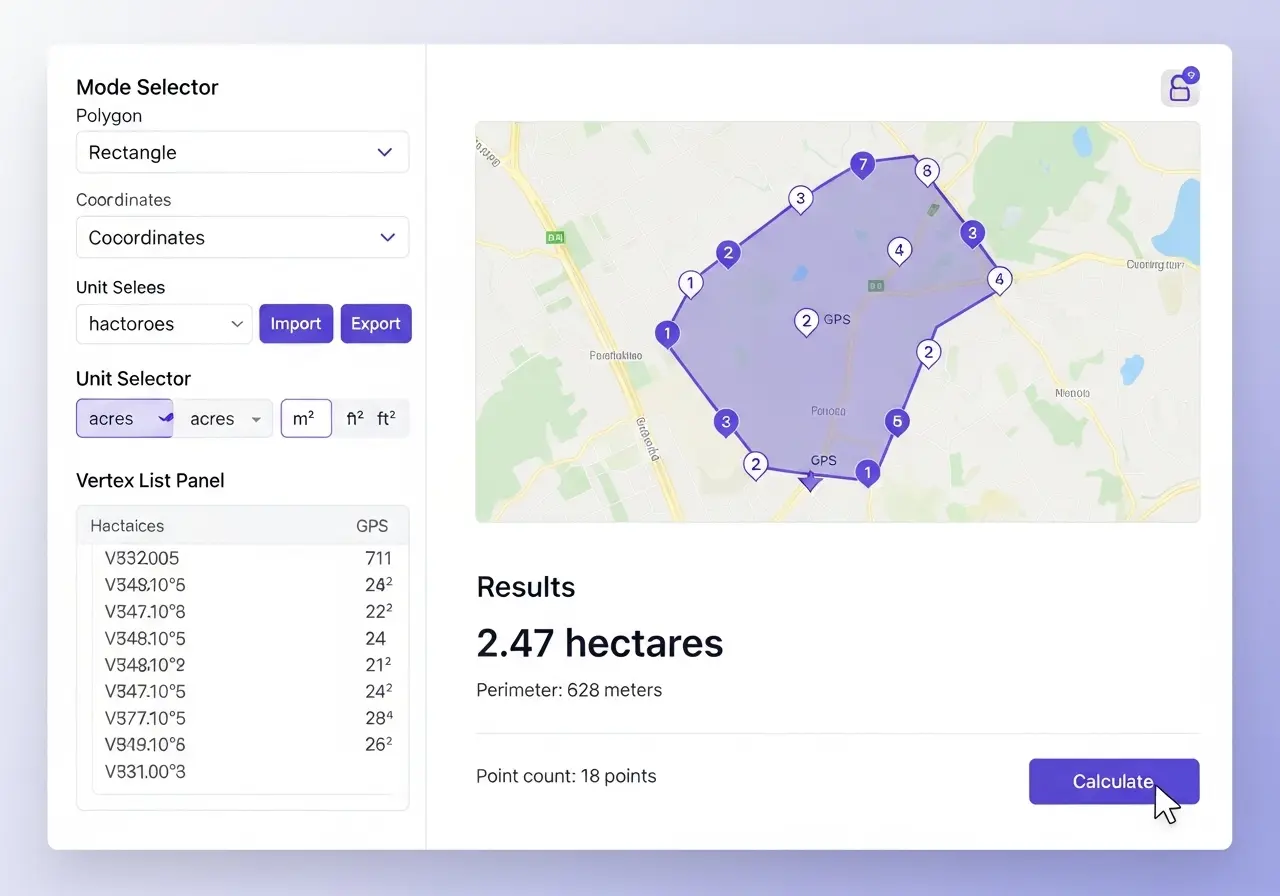
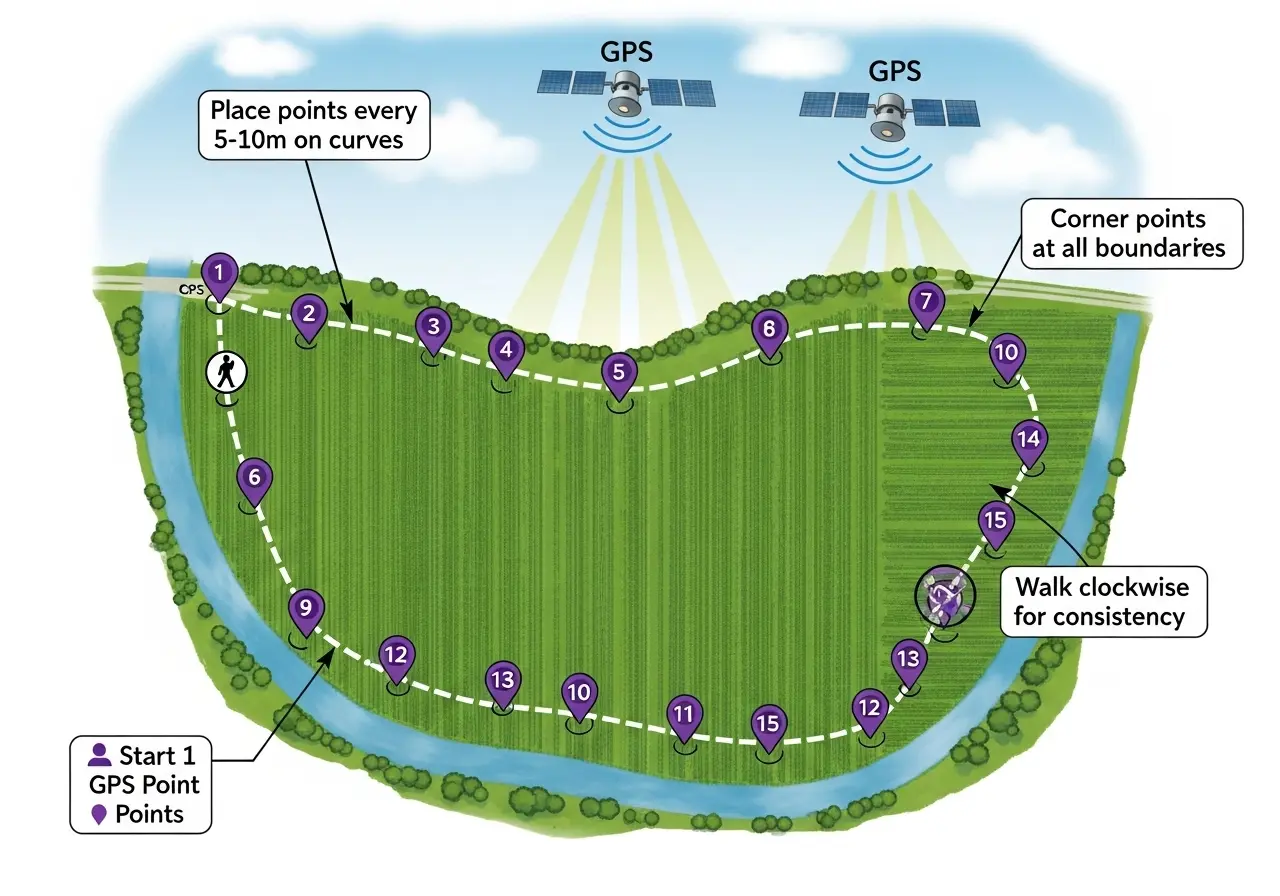
Minimum 3 points for a basic triangle, but more points increase accuracy significantly. For irregular plots, take points every 10-15 meters along straight boundaries and every 5 meters on curves. A typical 2-hectare field needs 15-25 well-placed points for 1-2% accuracy. Professional surveying often uses 50+ points for complex boundaries. Remember: more points on curves, fewer on straight lines.
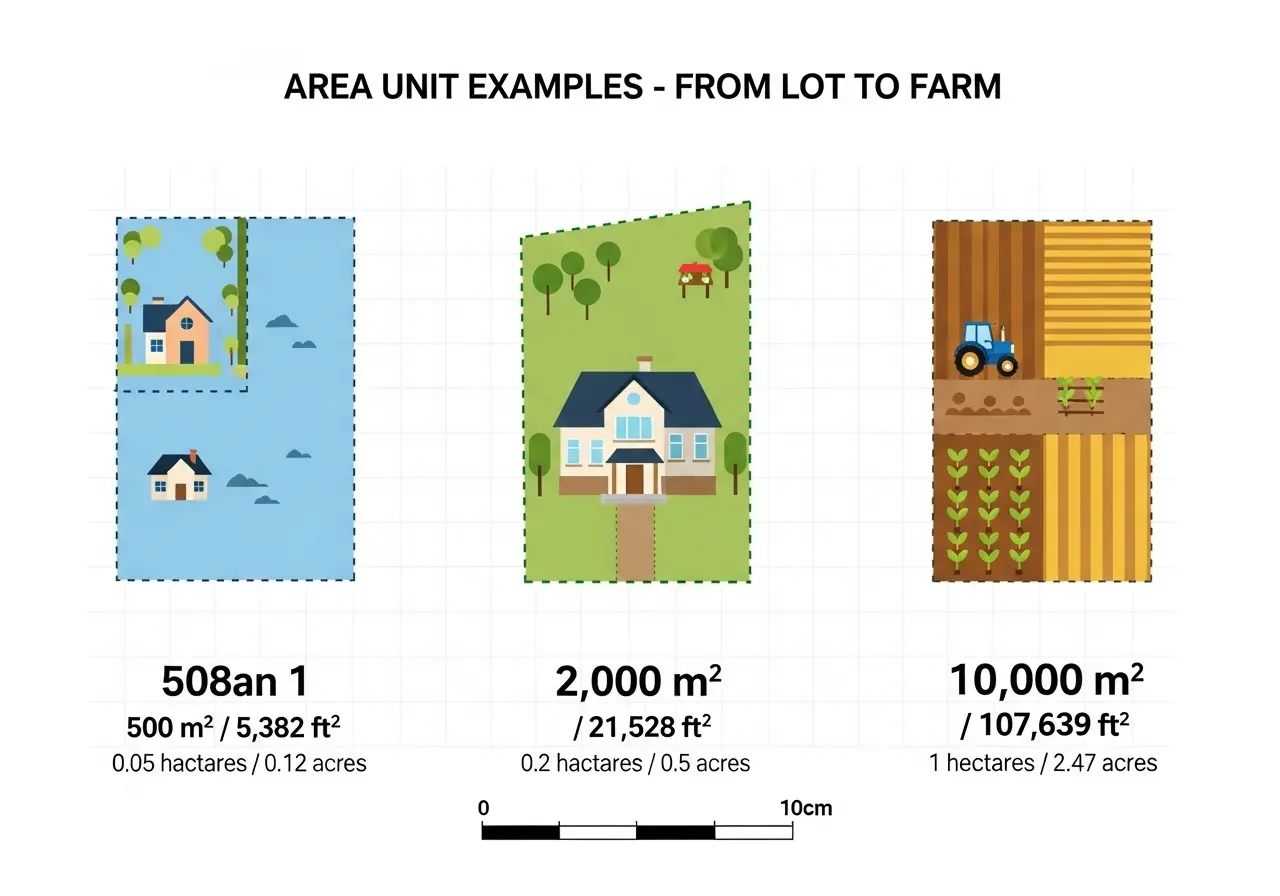
Hectares are the metric standard (1 ha = 10,000 m²) used internationally for agricultural land. Acres are the imperial unit (1 acre = 43,560 ft²) primarily used in the USA, UK, and former British territories. One hectare equals approximately 2.471 acres. Most modern calculators let you instantly convert between both units, so choose whichever is standard in your region.
It depends on the calculator. Most field area calculators work completely offline once loaded—you can add coordinates manually or via map clicks without internet. However, satellite map tiles require internet to display. GPS coordinate collection through your phone works offline (GPS is satellite-based, not internet-based), but loading maps for visual confirmation requires connectivity. Save your measurements locally for offline access later.
Modern smartphone GPS is accurate to 3-10 meters under optimal conditions (clear sky, open area). This provides 1-3% accuracy for fields larger than 0.5 hectares—sufficient for most agricultural, real estate, and residential purposes. Accuracy decreases under tree cover, near buildings, or in valleys. For legal boundaries or expensive transactions, consider using an external GPS receiver ($150-$300) that achieves sub-meter accuracy.
Yes, using the interactive map feature. Simply locate your property on the satellite imagery, then click around the boundaries to create a polygon. The calculator uses map coordinates to compute area. This method works well when you can clearly identify boundary markers, fences, or property corners on satellite imagery. However, GPS field walking provides higher accuracy for irregular or poorly marked boundaries.
Most calculators accept CSV (comma-separated values) files with latitude/longitude pairs, and GPX (GPS Exchange Format) files exported from GPS tracking apps. Standard format is: "latitude, longitude" on each line. Some advanced calculators also accept KML (Google Earth format) and GeoJSON files. Always verify your file's coordinate system matches the calculator's expectations (typically decimal degrees, WGS84 datum).